Decline Rate Types
There are four types of decline rate that can be specified:
- Annual Effective % (Secant)*
- Annual Nominal %
- Monthly Effective % (Secant)*
- Monthly Nominal %
Click image to expand or minimize.
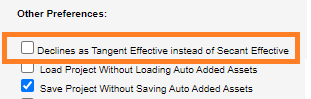
*For the Annual and Monthly Effective decline rate types, Enersight uses the Secant method by default but there is a User Preference to use the Tangent method.
Nominal Declines refer to the instantaneous decline rate at the start of the decline segment. This is the decline rate that is entered into the decline equations, for example an exponential decline with a 20% Annual Nominal decline is described by the equation q(t) = qi * e-0.2t, where t is time in years.
Hyperbolic Decline
q(t) = qi / [Di*b*(t-0.5) +1]^(1/b)
Where: qi = initial rate
Di = Nominal decline rate
b = hyperbolic exponent
t = time in days (note the ½ day rule)
q(t) = average rate for day t
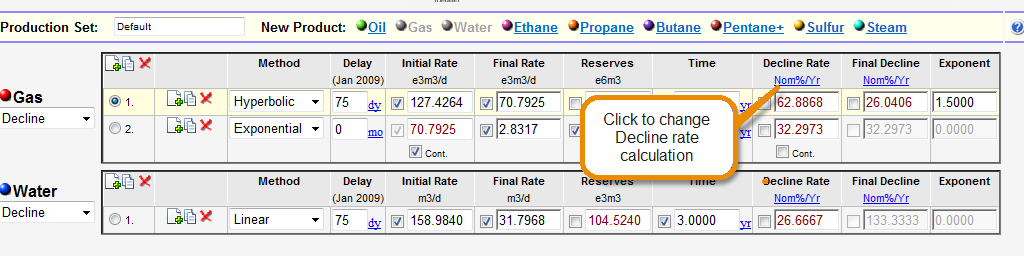
Enersight will convert between the four decline types when the decline rate type is toggled on the Decline tab by clicking on the link above the decline parameters.
