Trap Volumetrics
Use the Trap Volumetrics calculation method to define the fluid in place as a function of rock volume information.
Rock Volume Type: Calculate Net Rock Volume by applying a Net to Gross Ratio to the Bulk Rock Volume. The Bulk Rock Volume may be a simple input or a calculation. The options are:
- Area * Height: Enter reservoir Net Pay (reservoir thickness contributing to production) to calculate volume.
- Input: Enter Bulk Rock Volume directly.
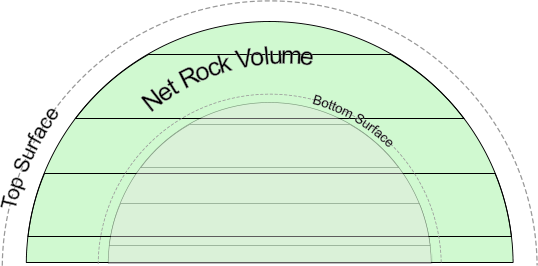
- Depth/Area Table: Calculate Bulk Rock Volume from reservoir area data at different depths. Use the Top Surface table to define the outer (upper) shape of the reservoir, and additionally use the Bottom Surface table to characterize the shape of the reservoir floor. Bulk Rock Volume will be calculated as the volume yielded by the first table minus its intersection with the volume yielded by the second table. Note that negative values are allowed to account for developments above sea level.
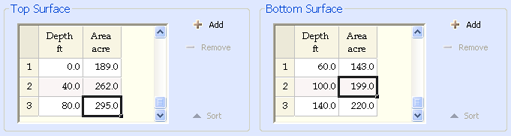
The Area Scaling variables below each table are factors that allows you to model possible deviations from the values in the tables; you can use distributions here to model uncertainty on reservoir volume in Monte Carlo and Reservoir Monte Carlo runs.
The following factors will impact the resulting fluid in place:
- Gas Cap Volume: Percentage of reservoir volume which is free gas. For
 oil reservoirs only.
oil reservoirs only. - Gas Oil Contact: (Only when the Depth/Area Table option is selected above.) Point (depth) of contact between oil and gas. For
 oil reservoirs only. Use this option to base the calculation on a known gas/oil contact point rather than known gas cap percentage. Note that negative values are allowed to account for developments above sea level.
oil reservoirs only. Use this option to base the calculation on a known gas/oil contact point rather than known gas cap percentage. Note that negative values are allowed to account for developments above sea level. - Porosity: Total net effective porosity of the reservoir.
- Oil / Gas Saturation: Initial main fluid saturation of the reservoir.
- Water Oil Contact: Point (depth) of contact between oil and water.
The following equations are used for calculating source and trap volumes:
Net Rock Volume = Bulk Rock Volume * Net to Gross Ratio
Reservoir Pore Space (Net Pore Volume) = Net Rock Volume * Porosity
Reservoir Gas Volume = Reservoir Pore Space * Gas Cap Volume
Reservoir Water Volume = (Depth - Water Oil Contact) * Area * Net to Gross Ratio * Porosity
Reservoir Oil Volume = (Reservoir Pore Space - Reservoir Gas Volume - Reservoir Water Volume) * Oil Saturation
Recoverable Oil = Reservoir Oil Volume * Recovery Factor / Bo
Solution Gas = Recoverable Oil * Initial GOR
where Initial GOR = initial gas-oil ratio, and Bo = oil formation volume factor; see Oil (Fluids).
For a  gas reservoir, it is assumed that the Z-factor corrected pressure (P/Z) is a linear function of cumulative production. The additional pressure and temperature information required for calculating the Z-factor is input in the Pressure Info Tab.
gas reservoir, it is assumed that the Z-factor corrected pressure (P/Z) is a linear function of cumulative production. The additional pressure and temperature information required for calculating the Z-factor is input in the Pressure Info Tab.
